In recent years, the discourse on sustainable materials has gained unprecedented momentum, paralleling the growing awareness of the ecological consequences associated with conventional plastics. Biodegradable materials have emerged as a beacon of hope, embodying the ethos of a circular economy and responsible resource utilization.Biodegradable materials encompass a diverse array of categories, each uniquely contributing to the reduction of environmental impact.
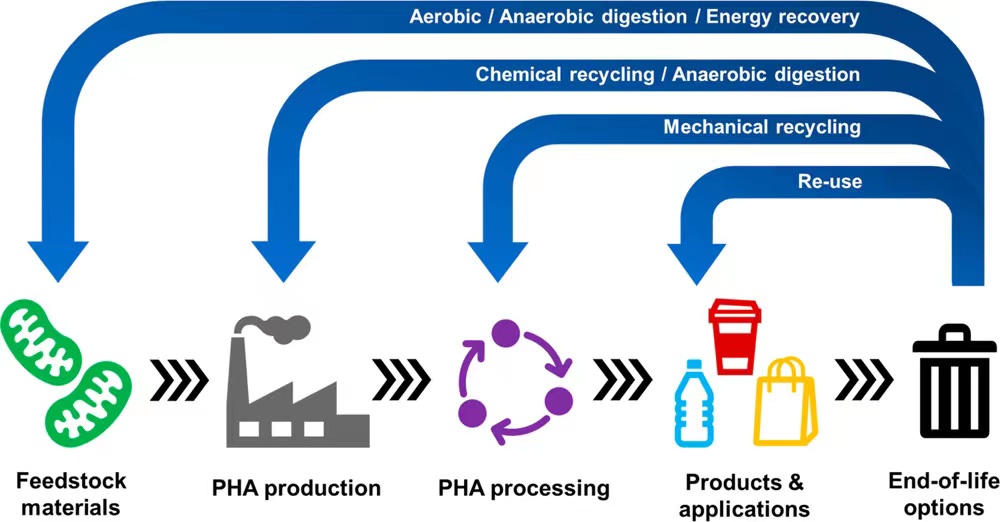
1.PHA
Polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA) are biodegradable polymers synthesized by microorganisms, typically bacteria, under specific conditions. Composed of hydroxyalkanoic acid monomers, PHA is notable for its biodegradability, renewable sourcing from plant sugars, and versatile material properties. With applications ranging from packaging to medical devices, PHA represents a promising eco-friendly alternative to conventional plastics, albeit facing ongoing challenges in cost-effectiveness and large-scale production.
2.PLA
Polylactic Acid (PLA) is a biodegradable and bioactive thermoplastic derived from renewable resources such as corn starch or sugarcane. Known for its transparent and crystalline nature, PLA exhibits commendable mechanical properties. Widely used in various applications, including packaging, textiles, and biomedical devices, PLA is celebrated for its biocompatibility and capacity to reduce environmental impact. As a sustainable alternative to traditional plastics, PLA aligns with the growing emphasis on eco-friendly materials in diverse industries.Production process of polylactic acid is free from pollution and the product is biodegradable. It realizes cycle in nature and is green polymer material.

3.Cellulose
Cellulose, derived from plant cell walls, is a versatile material increasingly gaining attention in the packaging industry. As a renewable and abundant resource, cellulose offers a sustainable alternative to conventional packaging materials. Whether sourced from wood pulp, cotton, or agricultural residues, cellulose-based packaging provides several advantages.Cellulose-based packaging is inherently biodegradable, breaking down naturally over time. Certain formulations can also be designed to be compostable, contributing to the reduction of environmental waste.Compared to traditional packaging materials, cellulose-based options often have a lower carbon footprint.
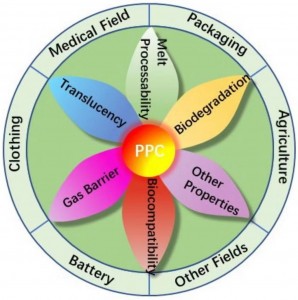
4.PPC
Polypropylene Carbonate (PPC) is a thermoplastic polymer that combines the properties of polypropylene with those of polycarbonate. It is a bio-based and biodegradable material, offering an environmentally friendly alternative to traditional plastics. PPC is derived from carbon dioxide and propylene oxide, making it a renewable and sustainable option. PPC is designed to be biodegradable under certain conditions, allowing it to break down into natural components over time, contributing to reduced environmental impact.
5.PHB
Polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB) is a biodegradable and bio-based polyester that belongs to the family of polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs). PHB is synthesized by various microorganisms as an energy storage material. It is notable for its biodegradability, renewable sourcing, and thermoplastic nature, making it a promising candidate in the quest for sustainable alternatives to traditional plastics. PHB is inherently biodegradable, meaning it can be broken down by microorganisms in various environments, contributing to reduced environmental impact compared to non-biodegradable plastics.

6.Starch
In the realm of packaging, starch plays a pivotal role as a sustainable and biodegradable material, offering environmentally friendly alternatives to conventional plastics. Derived from plant sources, starch-based packaging aligns with the global effort to reduce the environmental impact of packaging materials.

7.PBAT
PBAT is a biodegradable and compostable polymer belonging to the family of aliphatic-aromatic copolyesters. This versatile material is designed to address environmental concerns associated with traditional plastics, offering a more sustainable alternative. PBAT can be derived from renewable resources, such as plant-based feedstocks. This renewable sourcing aligns with the goal of reducing dependence on finite fossil resources. And it is designed to biodegrade under specific environmental conditions. Microorganisms break down the polymer into natural byproducts, contributing to a reduction in plastic waste.
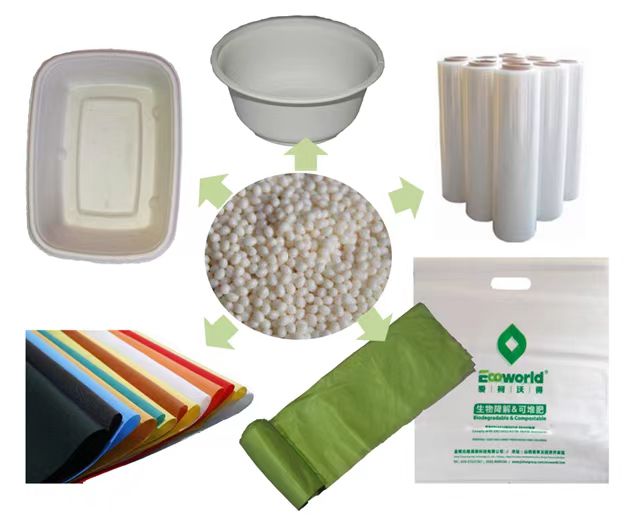

The introduction of biodegradable materials marks a significant shift toward sustainable practices in various industries. These materials, derived from renewable sources, have the inherent ability to naturally decompose, reducing environmental impact. Notable examples include Polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA), Polylactic Acid (PLA), and Polypropylene Carbonate (PPC), each offering unique properties such as biodegradability, renewable sourcing, and versatility. Embracing biodegradable materials aligns with the global push for eco-friendly alternatives to traditional plastics, addressing concerns related to pollution and resource depletion. These materials find applications in packaging, textiles, and medical devices, contributing to a circular economy where products are designed with their end-of-life considerations in mind. Despite challenges like cost-effectiveness and large-scale production, ongoing research and technological advancements aim to enhance the viability of biodegradable materials, fostering a more sustainable and environmentally conscious future.
Post time: Dec-07-2023
